Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Tanaka & Kataoka Lab.
Image-Based Diagnosis of Pathogenic Microorganisms using Colony Fingerprinting
In recent years, the field of bioimage informatics, which involves processing and analyzing biological image data using computational methods for automated and quantitative evaluation, has gained significant attention in biological and medical research. This technology enables objective and reproducible analysis of data that were previously evaluated subjectively, allowing for the processing of image information on an unprecedented scale.
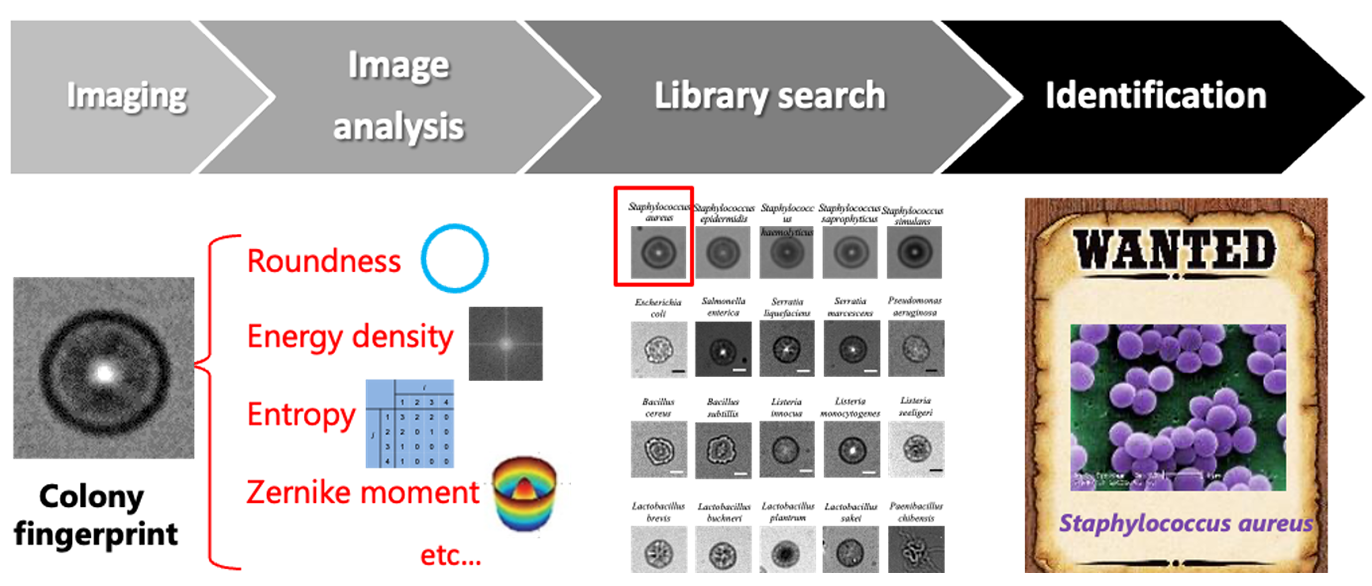
Our laboratory is working on the development of a “Colony Fingerprinting (CFP)”, a technique that combines bioimage informatics with machine learning to identify microbial species based on images of colonies formed during their growth. Unlike conventional microbial identification methods, which require multiple steps and are often costly, the CFP completes the identification process solely through image analysis. As a result, it offers a low-cost, rapid, and automated pathogen detection system with potential applications in various fields, such as environmental assessment, medical diagnostics, and food production management (Fig. 1).
Our laboratory has successfully developed an integrated CFP system that combines an imaging device capable of capturing areas over 1,500 times the field of view of a conventional microscope in just a few seconds with a cultivation apparatus. This system enables real-time imaging of microorganisms directly on Petri dishes during their cultivation process (Fig. 2).

Furthermore, by combining this system with machine learning technology, we have successfully identified as many as 20 microbial species based solely on image data. Currently, we are working on further improving the device and machine learning algorithms, as well as expanding the range of microbial species targeted for analysis, to advance the practical application of this system (Fig. 3).
