Core technology1
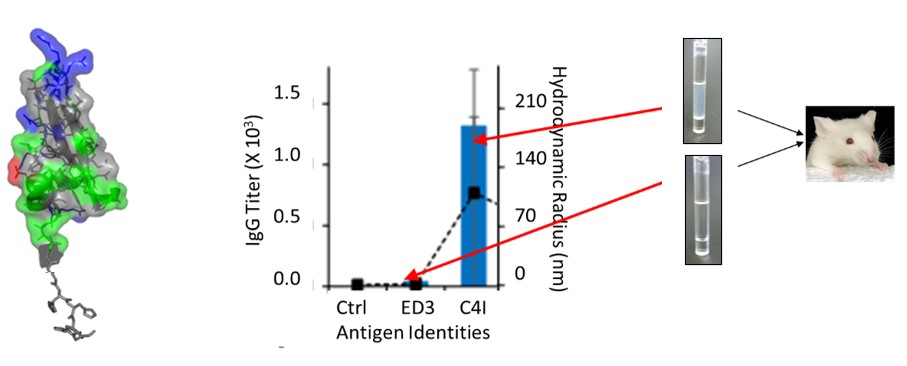
The SCP tag is a central piece of πBIO. Vaccine seeds developed by πBIO differ from conventional vaccines in that it uses not the virus itself but a fragment of the viral protein. The protein is expressed in E. coli and purified to a high purity, and used as the vaccine antigen. Protein fragments expressed in E. coli are inorganic molecules, non-toxic, and have overwhelming advantages over conventional vaccines in terms of safety, price, and development speed. However, the immunogenicity of recombinant proteins expressed in E. coli most often weak, making it unfit to use them as vaccine antigens. Therefore, to date, there is no subunit vaccine using proteins expressed in E. coli as antigens. SCP tag is the central technology of πBIO. SCP tag dramatically improves the immunogenicity of proteins and induces the generation of antiserum with neutralizing ability. In addition to the SCP tag, πBIO also includes methods to identify and produce viral proteins without affecting their structure and function, as well as methods to rapidly generate monoclonal antibodies.
Core technology2
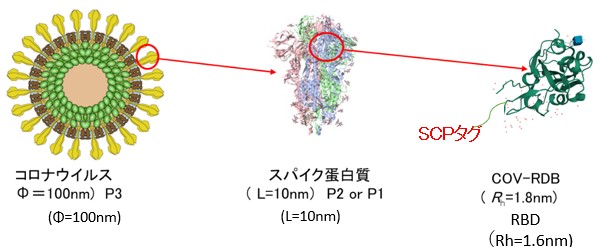
Focus on the Receptor Binding Domain(RBD) of their spike protein that allow viruses to bind to host cells. RBD is created by protein engineering. The addition of a SCP tag consisting of a few residues to RBDs enhances immunogenicity and induces immune memory. Anti-RBD serum is a prime vaccine seed candidate because of its neutralizing ability.
πBIO platform
Central technologies of πBIO are the fragmentation viral proteins, the enhancement of their immunogenicity, and their usage in pharmaceuticals and other products. The advantages of using πBIO include the following.
- Safety:High safety because only a part of the viral protein is used instead of the virus itself.
- Cost:Large scale at a low cost is possible for expression in E.coli.
- Development period:At πBIO, standard protocols are in place for the production, physical properties, and immunogenic analysis of recombinant proteins, and efficient development can be achieved in a short period of time.
- Effectiveness:The πBIO targets regions that are critical for viral infection such as the RBD. RBD has an epitope region(antibody recognition site) and is the binding site to the host cell receptor. As a result, when the fragment is used as a vaccine antigen, it has a high potential to induce an immune response with neutralizing ability.
- Handling:Proteins are inorganic molecules and are easy to handle as it can be stored under refrigeration.
- Use:It can be used for various applications as a platform technology(πBIO)
Examples of various applications
- ①Subunit vaccines:Vaccines are developed in a short period of time by using subunits as vaccine seeds.
- ②mRNA/DNA vaccines:Design gene sequences at the level of subunits with enhanced immunogenicity and incorporate them into mRNA/DNA vaccines.
- ③Monoclonal antibodies:Monoclonal antibodies, a byproduct of subunit vaccine development, will be applied to developing antiviral agents and test kits.
Patents and intellectual Property Rights
- ①Technology for inexpensive expression and purification of subunits by E.coli and ensuring quality and safety control(related to 1 design, generation, and properties on the previous page)
- ②Technology to enhance immunogenicity of subunits(related to 2 immunogenicity on the previous page
- ①Patent No.6986261:"Method for improving expression and yield of recombinant polypeptides", Application date:December 22, 2017
- ②Patent No.5273438:"Solubility calculation method for peptide-added biomolecules, and method for designing peptide tags and preventing inclusion body formation using the method", Application date:January 11, 2018(2)
- ➂Patent No.7194442:"Antigen composition", Application date:August 6, 2018