・Cell Science for Disease Prevention
・Pre-diabetes Model Cells and Mice
・Ideas for Cell Activators and Activated Cells
・Intercellular Molecular Communication Analysis
・Regulatory Science
・page top

News (2025.4)
◎"Extracelluar vesicles derived from stemness-high cells can suppress the metastasis" was demonstrated also with Nanog-overexpressing colon cancer cells.
◎ Effect of suppressing melanoma metastasis of extracellular vesicles secreted from iPS cells and Nanog-overexpressing cells ⇒suggesting that these anaplastic cells act as disease-preventing cells.
◎A novel role of Nanog was reviewed focusing the possibility of cancer metastasis prevention vaccine using extracellular vesicles.
◎Moderate hyperglycemia could suppress the metastasis of melanoma cells to liver .
◎Extracellular vesicles derived from melanoma with high metastatic potential suppressed the metastasis.
◎"NANOG overexpression is an enhancer of the metastatic potential of melanoma" was demonstrated for the first time.
■Cell Science for Disease Prevention using PreDMoC
・Cell Science for Disease Prevention
・Pre-diabetes Model Cells and Mice
・Ideas for Cell Activators and Activated Cells
・Intercellular Molecular Communication Analysis
・Regulatory Science
・page top
We are developing pre-disease models for clinical studies (PreDMoC) by gene modification and regenerative cell technology.
Using these models,we are engaged in research subjects focused on how to prevent the progress of diseases (Fig. 1), e.g.from pre-diabetes to diabetes,
immunodeficiency, inflammation, and cancer metastasis.
In the pre-disease stage, healthy cells are contacting a few disease cells. In the early stage of cancer metastasis, for instance,
a few cancer cells contact cells of healthy tissues. In order to analyze the intercellular molecular communication at the frontier of
such heterogeneous cell contacts, a unique single-cell analysis method has been developed.
Dynamic expression of whole connexin family was analyzed comprehensively and Cx30.3 was found to be a unique isoform with specific novel
functions such as a undifferentiated state marker and
a cell-cell contact-activated expression.
We also focus the potential novel functions of exosomes relevant to intercellular communication between remote cells.
|
 |
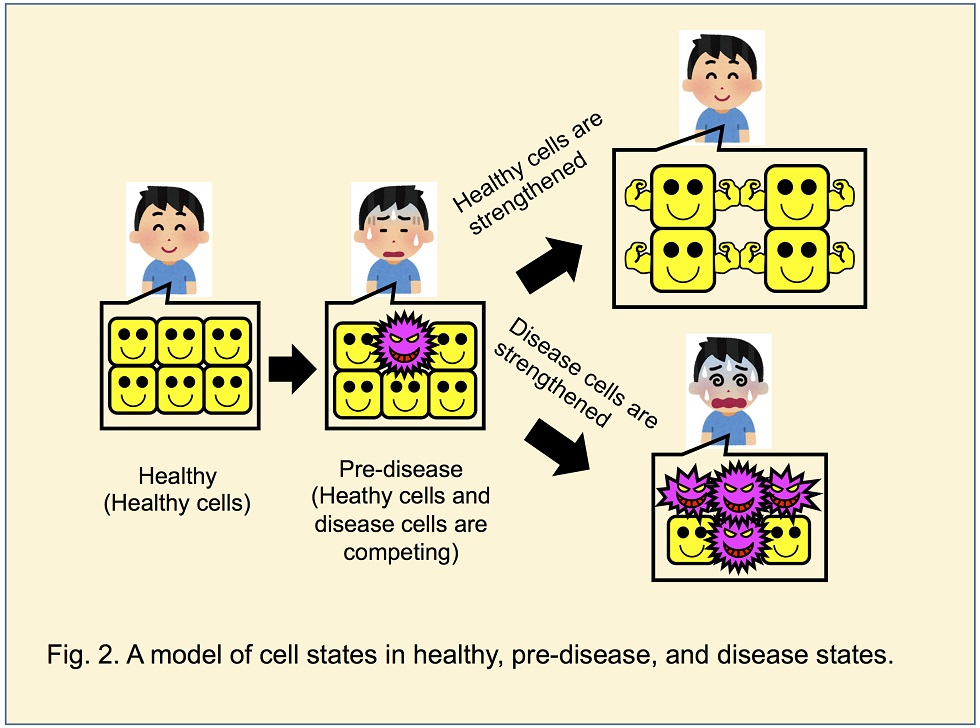
Disease progression is not necessarily a gradual and slow worthening process. It occasionally is a rapid and stepwise
worthening one. A sign of such a rapid worthening will be found in the pre-disease stage. During the pre-disease stage, healthy
cells and disease cells are competing. When the disease cell mass and malignancy surpass the preventive potential by healthy cells,
a rapid and stepwise worthening occurs.
The purpose of “Cell Science for Disease Prevention” is to detect and analyze the disease-healthy competing state and to find an
efficient way to be a healthy state. Research subjects are the survey of molecular markers for quantitative expression of disease-healthy
competing state, the threshold analysis of healthy to disease conversion, and the development of methods to strengthen healthy cells.
|
 |
Research titles currently in progress are
“Threshold analysis of healthy to disease conversion in pre-diabetes” , “Analysis of the resistivity against the
metastatic growth of melanoma cells” .
■Pre-diabetes Model Cells and Mice
Cell Science for Disease Prevention
・Pre-diabetes Model Cells and Mice
・Ideas for Cell Activators and Activated Cells
・Intercellular Molecular Communication Analysis
・Regulatory Science
・page top
Diabetes model mice generated spontaneously are commercially available but not
appropriate for the study to investigate the progress of diabetes. Therefore, we developed a model mouse and a model cell library by
knocking out or knocking down a principal cause gene(s) to simulate the pre-diabetes state.
Eight genes were selected as diabetes-related genes: (Pdx-1, Irs-1, Kir6.2, Irs-2, Gk, Shp,
Hnf-1α, Hnf-1β). One or two of them in ES cells were knocked down by RNAi method or knocked out by gene targeting method.
In total 38 knocked-down or overexpressing model cell lines were developed.
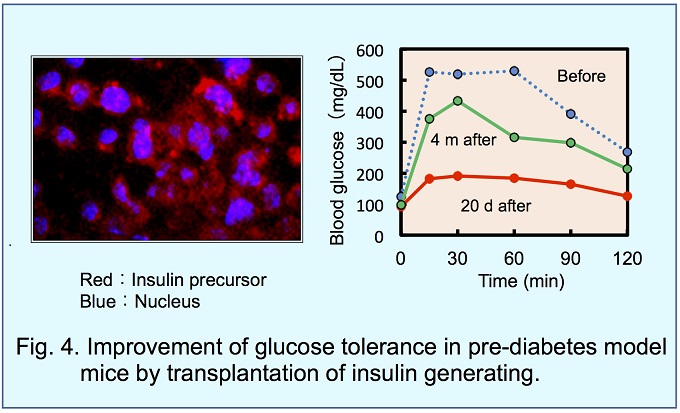
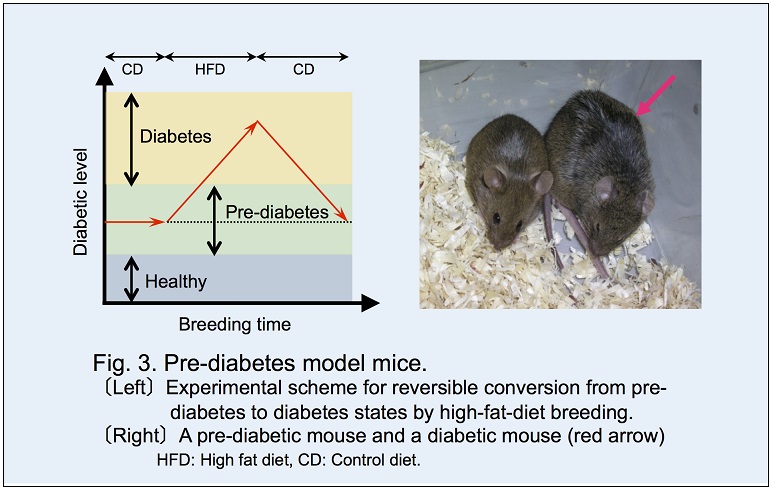
Moreover, Gk knocked-out mouse was developed and registered as B6;129-Gcktm1Tms. The casual blood glucose level and glucose
tolerance in this mouse showed a middle level between those of healthy and diabetic mice. Bred with high fat diet, this mouse became diabetes.
Therefore, this Gk(+/-) line was
defined as a pre-diabetes model mouse (Fig. 3).
|
 |
■Ideas for Cell Activators and Activated Cells
Cell Science for Disease Prevention
・Pre-diabetes Model Cells and Mice
・Ideas for Cell Activators and Activated Cells
・Intercellular Molecular Communication Analysis
・Regulatory Science
・page top
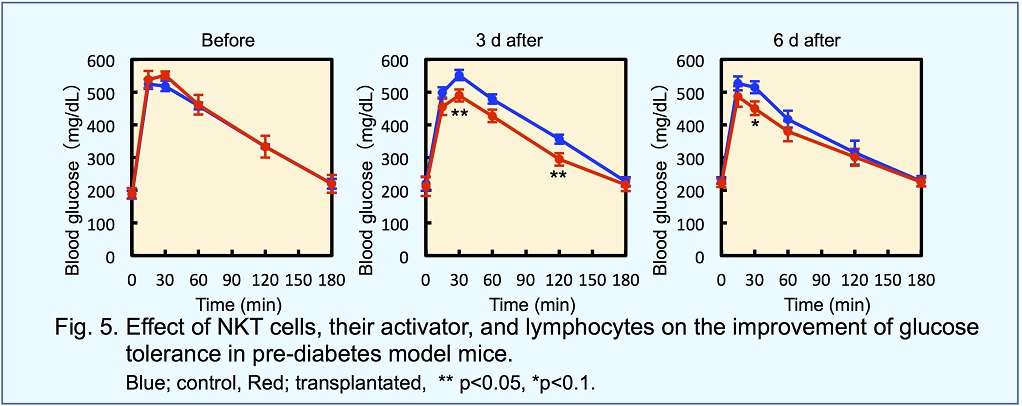
Insulin generating cells for diabetes patients, and NKT cells and lymphocytes for immune therapy may be called
as cell medicine if they are effective for the therapy.
In contrast, if healthy cells are strengthened and prevent the invasion
of disease cells, the healthy cells are effective for the therapy. Not only the transplantation of these strengthened cells but
also the injection of factors that may strengthen healthy cells in vivo is promising.
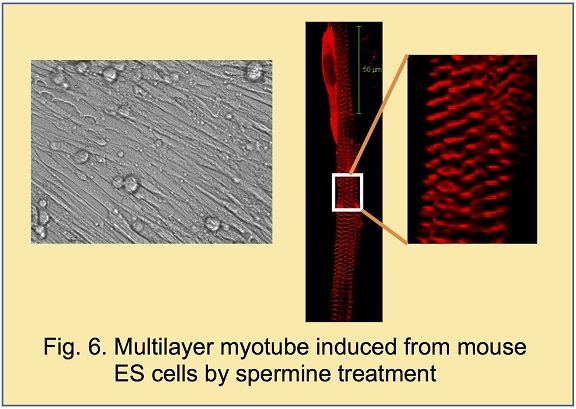
Mouse ES cells were cultured by hanging drop method to obtain embryoid bodies. When spermine was added to embryoid bodies,
peripheral and frontier cells were killed. To our surprise, skeletal muscle cells showed
3-dimensional growth (Fig. 6).
Spermine was originally recognized as a growth inhibitor of muscle cells. In fact, frontier cells were killed. However, a marked
growth of muscle cells occurred successively and there appeared a large number of spherical cells that were thought to be stem cells
of muscle tissue. In this case, spermine may be regarded as a cell activator.
Skeletal muscle chipshowed an insulin responsive glucose uptake.
|
 |
■Intercellular Molecular Communication Analysis
Cell Science for Disease Prevention
・Pre-diabetes Model Cells and Mice
・Ideas for Cell Activators and Activated Cells
・Intercellular Molecular Communication Analysis
・Regulatory Science
・page top
In multicellular organisms, highly integrated functions are fulfilled by intercellular communication between various cells
via complicated networks. The basic process, however, is the communication between 2 cells. Communicated signals are molecular
(chemical signal), electrical, electrochemical, and mechanical. These signals need to be measured by quantitative, real time, and
non-invasive analytical methods.
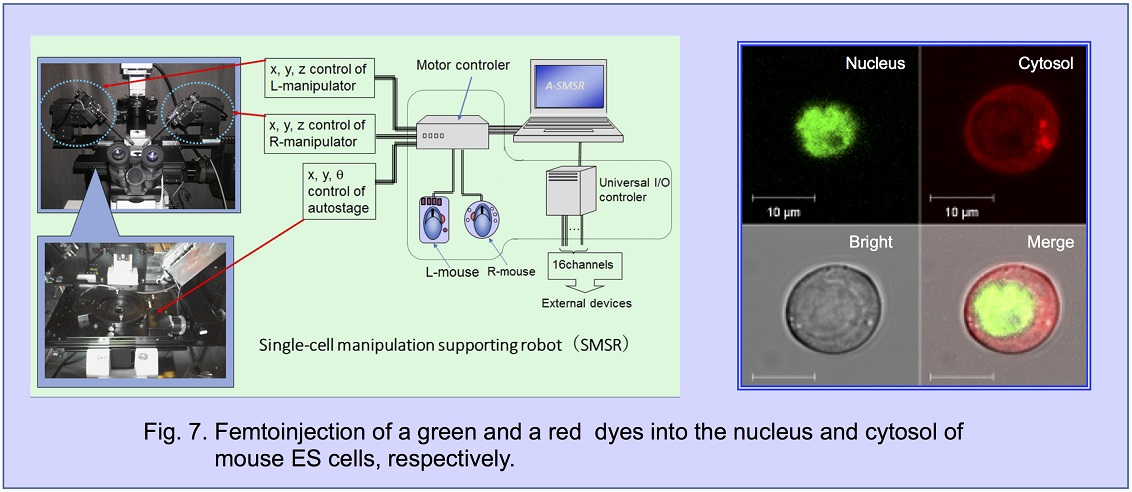
A microelectrode with a tip diameter smaller than 1 μ was devised and then extended to 3-channel. This multi-functional
microelectrode system was useful for simultaneous measurements and controls.
They are injection of molecules into single-cells, electric potential measurement, ion concentration measurement, in vivo measurement
of electrical impedance of an intercellular membrane, and application of electric potential to cell membrane.
A microelectrode with a tip diameter smaller than 1 μ was devised and then extended to 3-channel. This multi-functional microelectrode
system was useful for simultaneous measurements and controls. They are injection of molecules into single-cells, electric potential
measurement, ion concentration measurement, in vivo measurement of electrical impedance of an intercellular membrane, and application
of electric potential to cell membrane.
Quantity of injected material can be controlled semi-quantitatively at femto-gram level and therefore, we called this technology
the femtoinjection. For the rapid and efficient femtoinjection, a useful supporting robot (Fig. 7) and a dish operating device
“Suguwaculture system” was developed.
This robot system is working only in our laboratory.
This technology is useful to target not only an isolated single-cell but also a single-cell in a multicell tissue, and therefore,
enables analysis of intercellular communication between a target single-cell and any surrounding cells in contact with the target cell.
In case of the contact of a cancer cell, for example, the healthy cell may generate an “alarm” signal and strengthen the guard against
the invasion of the cancer cell. Such a dynamic behavior of healthy cells may be analyzed by the femtoinjection system.
■Regulatory Science
Cell Science for Disease Prevention
・Pre-diabetes Model Cells and Mice
・Ideas for Cell Activators and Activated Cells
・Intercellular Molecular Communication Analysis
・Regulatory Science
・page top
Regulatory Science is
(1)Toxicological science for the decision of regulation
(2)Scientific management to fulfill regulation values
(3)Analytical science to confirm the fulfillment of regulation values
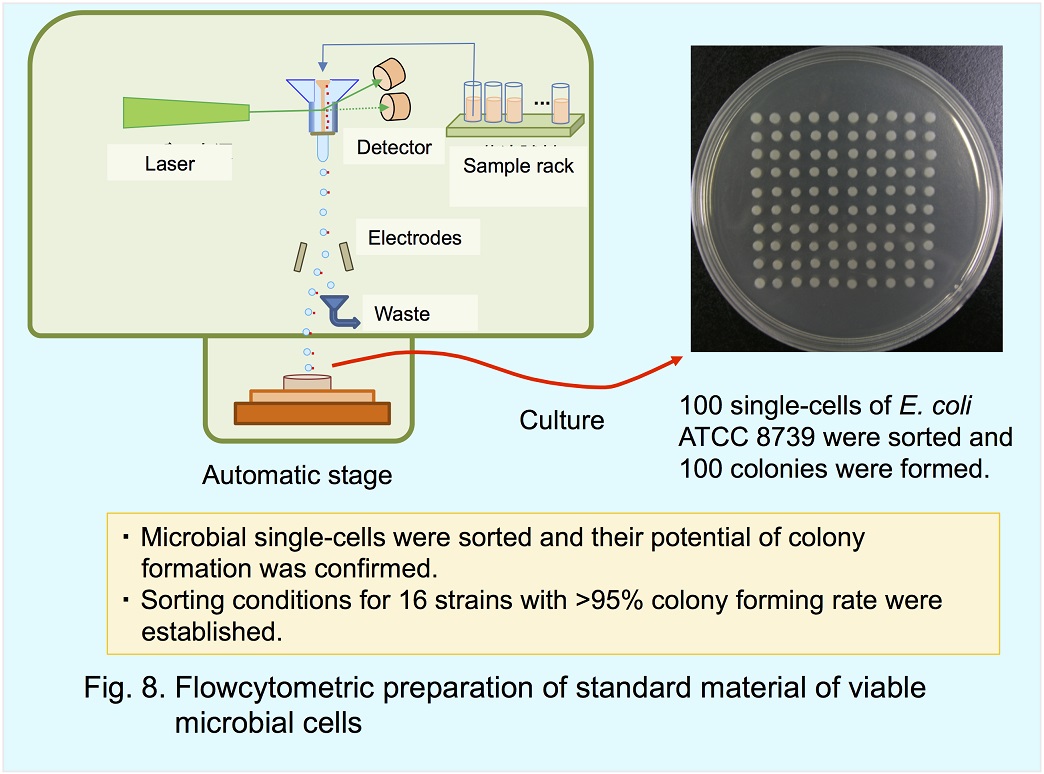
We are engaged in regulatory science for the food safety and the validation of microbiological tests. One of the research subjects is
stanard material of viable microbial cells.Preparation of single-cell with colony forming potency was demonstrated using a cell sorter (Fig. 8).
Rapid decision is important in (3). 2NBDG was developed for the photometric rapid detection of glucose uptake by viable cells. Density slicer was
developed for the efficient separation of viable cells from food matrices, which was essential for non-culture rapid methods. Automatic system was
developed for the simultaneous measurement of 3D-images of every colony in multiple plates.
The selection of indicators for toxicity evaluation is important in (1). From the viewpoint of bioethics, the pain suffered by animals during toxicity
tests should be as small as possible. The toxicity may be evaluated from the slight effects by small quantity of materials on the pre-disease state.
In this sense, pre-diabetes model mice are more sensitive than diabetes model mice in the evaluation of active factors that may improve or worthen
blood glucose tolerance.
|
 |