Mitsunori Tarao, PhD

|
|

|
| In the Salzkammergut, Austria |
In the West Bengal,
India |

|
|

|
| In the Salzkammergut, Austria |
In the West Bengal,
India |
Almost all biomass on our earth is composed of microorganisms and plants. They play major role in global material cycles involved with organisms, while animals are not always indispensable for them. Human beings, however, disturb and intercept material cycles in spite of their quite insignificant amount of biomass, resulting in their own crisis of extinction. The purpose of my research is to pursue rational way of ecosystem management for our sustainable survival by understanding roles of microrganisms in natural environments.
Recent studies are as follows:
- Biodegradation of xenobiotics
There are a plenty of microorganisms capable of degradation of xenobiotics in natural environments, while pollutants often remain at quite low level for a long period. Some xenobiotics of low concentration disrupt endocrine system or are bioaccumulated resulting in toxic effects on human beings. We need to elucidate environmental factors, which limit metabolic activities or survival of degrading microorganisms, such as nuturients concentration, xenobiotics concentration, predator, soil absroption, etc. These studies may give useful information for bioremediation.
- Evaluation of reliability of biological indicators of faecal pollution
I evaluate reliability of biological indicators of faecal pollution, snch as total coliform, Escherichia coli, or faecal streptococcus, especially in tropical region by comparison with molecular marker, faecal sterols. The research is collaborated with the laboratory of organic geochemistry (Dr. Takada's lab.).
- Microbial food chain as the essence of food chain
- Studying about effects of microbial food chain on biomass, respiration, denitrification, or survival of microorganisms (ex. see below).
- Studying about effects of microbial food chain on carbon or nitrogen balance in soil.
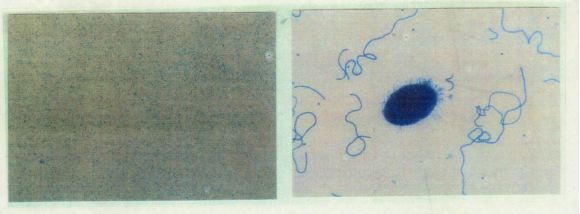
Pseudomonas sp. strain DP-4 in pure culture (left)
or mixed culture with Tetrahymena thermophila (right).
Furthermore, I always tell my stutents the importance of paying attention to structure and function of our society and social affairs as cause of environmental problems.
- Ozaki, H. et al. (2013) Human factors and tidal influences on water quality of an urban river in Can Tho, a major city of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Assess. 185 (in press)
- Kido, F., and M. Tarao (2013) Effect of water temperature, and the concentration of phosphorus or nitrogen on the concentration of chlorophyll a in an experimental pond in which water purification was performed by phosphorus absorbent and porous concrete blocks. People & Environ. (Ningen to Kankyo) 39: 2-10. (in Japanese with English summary)
- Hahn, M.W., E. Lang, M. Tarao, and U. Brandt. (2011) Polynucleobacter rarus sp. nov., a free-living planktonic bacterium isolated from an acidic lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 61: 781-787. (doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.017350-0)
- Tarao, M., J. Jezbera, and M.W. Hahn (2009) Involvement of cell surface structures in size-independent grazing resistance of freshwater Actinobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75: 4720-4726. (doi: 10.1128/AEM.00251-09)
- Mitsuhori, J., M. Seto, and M. Tarao (2009) A system for the nitrogen removal from groundwater by using porous concrete blocks. People & Environ. (Ningen to Kankyo) 35: 54-59. (in Japanese with English summary)
- Tarao, M., N. Takeda, and M. Seto (2008) Respiration and carbon balance of the bacterium Pseudomonas sp., a protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila, and a fungus Trichoderma viride in a food chain system with glass beads. Microbes Environ. 23: 244-247. (doi: 10.1264/jsme2.23.244)
- Matsuno, K., M. Tarao, and M. Seto (2008) Effect of protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila or fungus Trichoderma viride on denitrification by bacterium Pseudomonas sp. strain DP-4 in the culture system with or without glass beads. Jpn. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. (Nihon Dojo Hiryo Gaku Zassi) 79: 69-75. (in Japanese with English summary)
- Tarao, M., M. Ikeuchi, and M. Seto (2006) Biodegradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol (TCP), density of TCP-degrader, and amount of dissolved organic carbon in solution of repeatedly applied with cow manure or chemical fertilizer. Man & Environ. (Ningen to Kankyo) 32: 141-144. (in Japanese)
- Shen, Y., M. Tarao, and M. Seto (2005) Validity of synthetic mineral medium to evaluate inorganic salts that limit survival of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in inland waters. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 31: 40-48. (in Japanese with English summary)
- Isobe, K.O., M. Tarao, M.P. Zakaria, H.C. Nguyen, Y.M. Le, and H. Takada (2004) Effect of environmental factors on the relationship between concentrations of coprostanol and fecal indicator bacteria in tropical(Mekong Delta) and temperate(Tokyo) freshwaters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70: 814-821. (doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.2.814-821.2004)
- Tarao, M., K. Matsuno, and M. Seto (2003) Effect of pH value on biomass and nitrogen, carbon balance of soil microbial community in glass beads column. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 29: 117-121. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M., Y. Yamashita, A. Sato, and M. Seto (2002) Effects of protozoa and glass beads on bacterial biomass and metabolism in a food chain system of glucose-Pseudomonas sp. strain DP-4-Tetrahymena thermophila. Microbes Environ. 17: 128-133.
- Isobe, K.O., M. Tarao, M.P. Zakaria, N.H. Chiem, L.Y. Minh, and H. Takada (2002) Quantitative application of fecal sterols using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to investigate fecal pollution in tropical waters: western Malaysia and Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36: 4497-4507. (doi: 10.1021/es020556h)
- Shen, Y., M. Tarao, and M. Seto (2002) Suppressive effect of visible light on the biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol or 2,4,5-trichlorophenol by Pseudomonas sp. strain DP-4. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 28: 2-9. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Matsunaga, J., M. Tarao, and M. Seto (2001) Remnant of 2,4-dichlorophenol(DCP) after degradation of low or high concentration of DCP by Pseudomonas sp. strain DP-4 in pure or mixed culture. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Microb. Ecol.(Nihon Biseibutsu Seitai Gakkai-shi) 16: 40-47. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M., and M. Seto (2000) Estimation of the yield coefficient of Pseudomonas sp. strain DP-4 with a low substrate (2,4-dichlorophenol[DCP]) concentration in a mineral medium from which uncharacterized organic compounds were eliminated by a non-DCP-degrading organism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 566-570.
- Tarao, M., M. Itoh, and M. Seto (1999) Second-order rate constants as affected by some environmental factors in pure culture system of 2,4-dichlorophenol-Pseudomonas sp. strain DP-4. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 25: 2-7. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Hosaka, T., M. Itoh, M. Tarao, and M. Seto (1998) Survival of Pseudomonas sp. strain DP-4 and biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol under extreme environmental conditions. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 24: 2-9. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Tarao, M., A. Yamasaki, and M. Seto (1997) Comparative studies on the degradation of high and low concentraions of 2,4-dichlorophenol and the changes in the density of degrader in several sample waters from aquatic environments. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 23: 146-155. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Tarao, M., K. Onozuka, and M. Seto (1997) A trial for the bioremediation in the water sampled from the lake Okutama contaminated with 2,4-dichlorophenol at low concentration. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 23: 74-81. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Tarao, M., T. Nakazawa, and M. Seto (1996) Comparative studies on the degradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol by Pseudomonas sp. strain DP-4 in liquid medium in soil with various amounts of organic carbon. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 22: 152-160. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Takeno, Y., M. Tarao, and M. Seto (1995) Comparative studies on the degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol by Pseudomonas sp.(DP-4) in liquid medium and in soil with various amounts of organic carbon. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 21: 126-133. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Tarao, M., S. Kurohata, and M. Seto (1995) Effects of low concentration of 2,4-dichloropheno(DCP) and auxiliary substrate on the degradation of DCP by Pseudomonas sp.(DP-4). Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 21: 61-67. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Matsumoto, K., R. Iida, M. Tarao, and M. Seto (1994) Comparative studies on the degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol or 2,4,5-trichlorophenol by a bacterial species of Pseudomonas sp.(DP-4). Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 20: 96-103. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Tarao, M., T. Honma, and M. Seto (1994) Co-metabolism of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol by a bacterial species of Pseudomonas sp.(DP-4). Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 20: 2-7. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Tarao, M., and M. Seto (1994) Comparative studies on biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in soil and in liquid medium. Soil Microorgnaisms.(Tsuchi to Biseibutsu) 43: 9-16. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Tarao, M., K. Tsunozaki, and M. Seto (1993) Biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol at low concentration and specific growth rate of Pseudomonas sp. strain DP-4. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Microb. Ecol.(Nihon Biseibutsu Seitai Gakkai-shi) 8: 169-174.
- Tarao, M., M. Tanaka, and M. Seto (1993) Reproducibility on degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol by inoculated Pseudomonas sp.(DP-4) in groundwater sample. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 19: 125-131. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Matsumoto, K., M. Tarao, M. Seto (1993) Biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in some soils. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 19: 68-74. (in Japanse with English summary)
- Tarao, M. (2010) Environmental Sciences for Humans and Society. Min-iren Iryo. 2010.5- (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M. (2009) Protection of intellectual property undermining publicness of national university corporations. J. Japanese Scientists (Nihon no Kagaku-sha) 44: 66-71. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M. (2006) LDP's proposal to rivision of the constitution and academic freedom. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 32: 65-66. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M. (2005) Problems of voting rights for Japanese citizens living abroad and a proposal for improvement. J. Japanese Scientists (Nihon no Kagaku-sha) 40: 678. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M. (2005) Mammoth ruling party resulted by election system. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 31: 153. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M. (2005) "Difference of temperature" among residents over recovery undertaking of illegal dumping site. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 31: 22-24. (in Japanese)
- Aoki, W., T. Ogawa, M. Tarao, and S. Tomoda (2004) Present situation of post-doctoral fellowship. J. Japanese Scientists (Nihon no Kagaku-sha) 39: 228-234. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M. (2003) Present situation and issues of agriculture in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 29: 28-31. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M. (2001) Mistrust in genetically modified plants. J. Japanese Scientists (Nihon no Kagaku-sha) 36: 604-605. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M. (2000) Problems on the innovative waste treatments whiche proposed by administration side. J. Japanese Scientists (Nihon no Kagaku-sha) 35: 175-179. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M., and H. Tarao (1999) Plastics recycle by autonomy service: present trend and a case study in Tamagawa Waste Treatment Corporation. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 25: 115-123. (in Japanese)
- M. Tarao (1998) Clean-up of polluted environment by microorganisms. Min-iren Iryo. 310: 62-63. (in Japanese)
- Tarao, M., and M. Seto (1996) Biodegradation of chlorinated phenol at low concentration and growth of degrader. Man & Environ.(Ningen to Kankyo) 22:23-37. (in Japanse)