RESEARCH ITEM A02
Study on Transport and Distribution of Aerosols and Air Pollutants in East Asia
Objective and Entire Framework
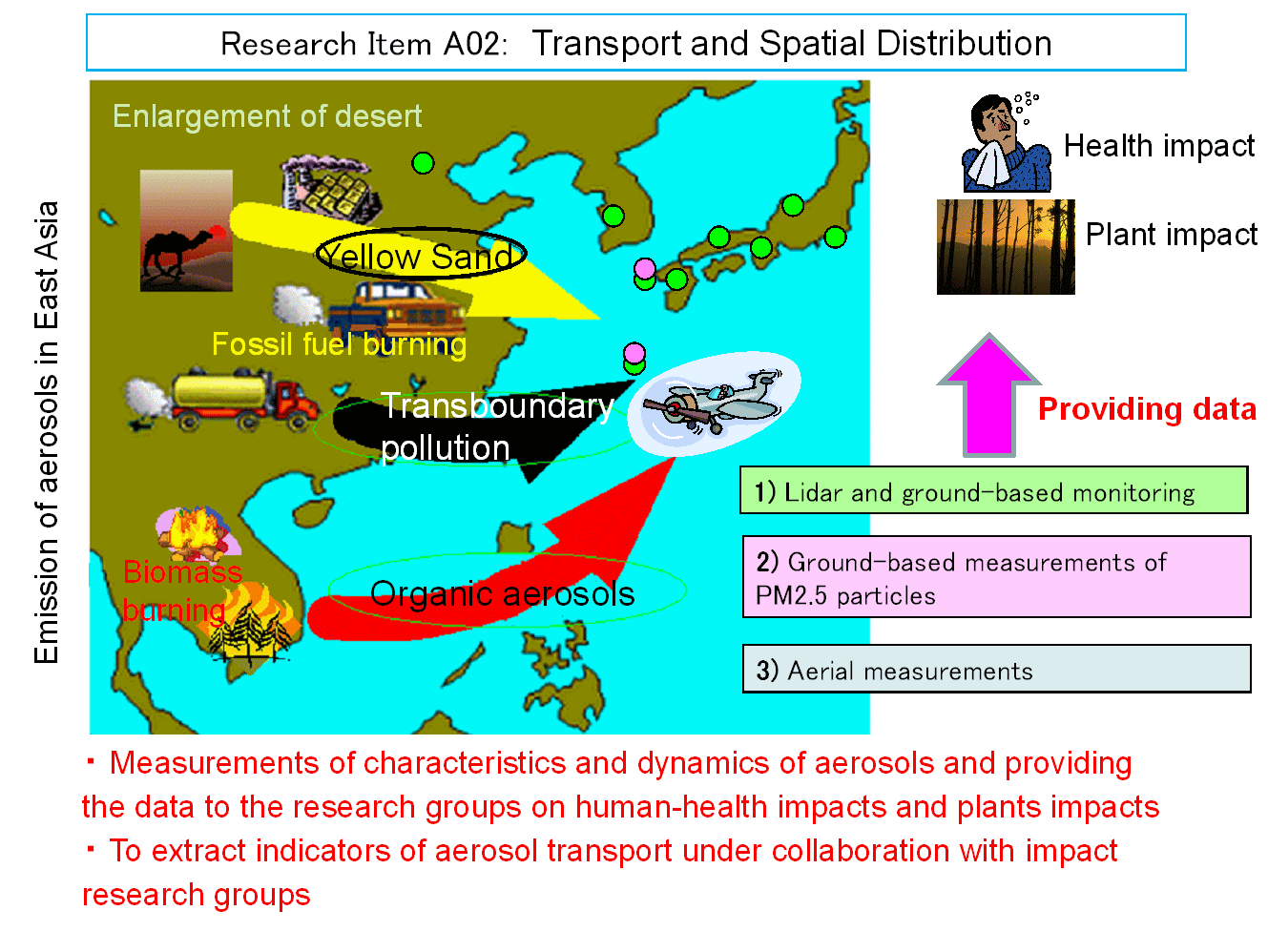
Research Item A02 aims at obtaining observational data on distribution, transport, and chemical characteristics of aerosols that can be applied to the studies of impact of aerosols on plants and human health in Research Items A03 and A04.
In East Asia, various kinds of aerosols emitted from anthropogenic and natural sources such as sulfate, nitrate, black carbon, organic carbon and mineral dust coexist as a mixture. To understand the effects of aerosols to plants and human health, it is indispensable to understand the characteristics and regional scale distribution and movement of aerosols.
In this study, three different approaches are taken in the three research groups (P05, P06, and P07). P05 employs the lidar network and ground-based measurement networks including the measurement in mountain regions to study the distribution and movement of aerosols in various spatial and temporal scales. In P06, the chemical and physical characteristics of aerosols are observed at the ground stations. In P07, observations using an aircraft are performed.
In A02, proposed researches are also conducted on behavior of specific pollutants, namely polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) (K04), nitrogen oxides (K05), and black carbon (K07), and on satellite remote sensing (K06)
Research Item A02 aims at obtaining observational data on distribution, transport, and chemical characteristics of aerosols that can be applied to the studies of impact of aerosols on plants and human health in Research Items A03 and A04.
In East Asia, various kinds of aerosols emitted from anthropogenic and natural sources such as sulfate, nitrate, black carbon, organic carbon and mineral dust coexist as a mixture. To understand the effects of aerosols to plants and human health, it is indispensable to understand the characteristics and regional scale distribution and movement of aerosols.
In this study, three different approaches are taken in the three research groups (P05, P06, and P07). P05 employs the lidar network and ground-based measurement networks including the measurement in mountain regions to study the distribution and movement of aerosols in various spatial and temporal scales. In P06, the chemical and physical characteristics of aerosols are observed at the ground stations. In P07, observations using an aircraft are performed.
In A02, proposed researches are also conducted on behavior of specific pollutants, namely polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) (K04), nitrogen oxides (K05), and black carbon (K07), and on satellite remote sensing (K06)
Main research content
Planned Research A02-P05
Study of Distribution and Movement of Aerosols Using Lidar and Surface Monitoring Networks
Study of Distribution and Movement of Aerosols Using Lidar and Surface Monitoring Networks
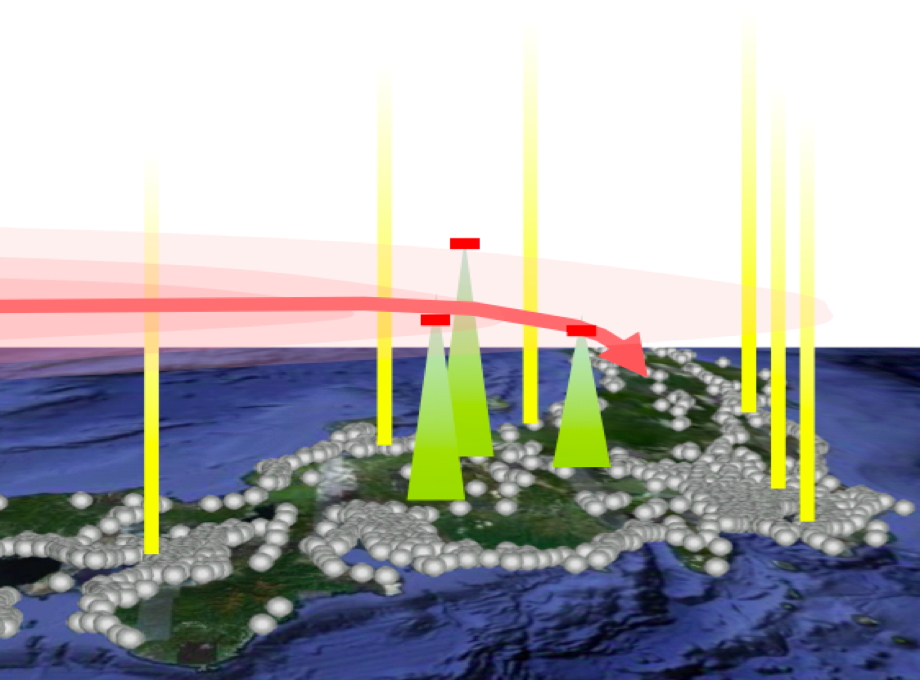
Three-dimensional distribution and movement of aerosols are studied using the lidar network, surface monitoring instruments in mountain area, the existing air pollution monitoring network, and chemical transport models, for understanding the emission, transport and deposition of aerosols in various spatial and temporal scales. The network of two-wavelength lidars constructed in the previous studies is used to observe three-dimensional distribution of aerosols. The lidars at primary stations are improved in this study to have nitrogen Raman scattering receivers at 607 nm for better characterizing light absorbing aerosols. Aerosol monitoring instruments are installed in the mountain area for validating the lidar measurements and for studying transport from free troposphere to the planetary boundary layer. The existing air pollution monitoring network data are also used in the study. The measured data are analyzed synergistically with the chemical measurement data in Research Item A02-P06 and the aircraft observation data in A02-P07. The observed data and the results of the analysis will be provided for the studies on aerosol impacts on plants and human health in A03 and A04.

Planned Research A02-P06
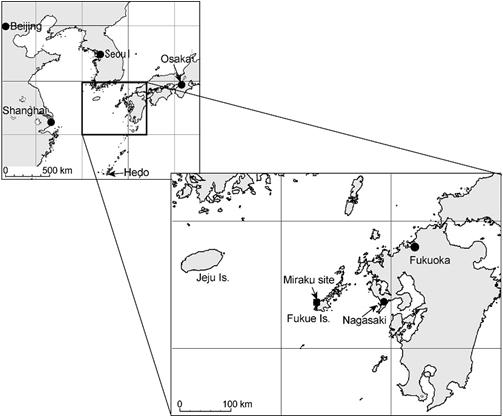
Field Study of PM2.5 and Harmful Substances to Human Health in Aerosols at Upwind Areas of Japan
Field Study of PM2.5 and Harmful Substances to Human Health in Aerosols at Upwind Areas of Japan
Particulate matters originating in East Asia will supposedly increase in
the near future, and there is much concern about their influence on Japan,
which is located on the leeward side of the westerlies. In this view, our
research group started a year-round measurement of PM2.5 and particulate
substances harmful to human health at upwind areas of Japan. Obtained data
in this study will be used in epidemiological surveys to be conducted in
the same area by A04 group. The followings are the instrumentations deployed
or to be deployed at the monitoring stations shown below.
a) PM2.5 and real-time aerosol monitors
b) Aerosol filter samplings
c) AMS: Aerosol Chemical Species Monitor (ACSM, Aerodyne) or Quadrupole Aerosol Mass Spectrometer (Q-AMS, Aerodyne)
d) Single-particle mass spectrometer
a) PM2.5 and real-time aerosol monitors
b) Aerosol filter samplings
c) AMS: Aerosol Chemical Species Monitor (ACSM, Aerodyne) or Quadrupole Aerosol Mass Spectrometer (Q-AMS, Aerodyne)
d) Single-particle mass spectrometer

Planned Research A02-P07
Aerial observation of chemical composition of aerosols transported from East Asia
Aerial observation of chemical composition of aerosols transported from East Asia
Anthropogenic emission in East Asia has been increasing due to the rapid
economic growth in this area. Atmospheric pollutants emitted in this area
are observed even in North America, and they affect northern hemispheric
climate. Not only in the global aspects but in regional aspects, long-range
transport of pollutants is very important. Transformation of pollutants
during the long-range transport is an important problem from a point of
view of regional air quality and acid rain. In order to evaluate the transport
of atmospheric pollutants from the East Asia and to analyze the transformation
processes during the transport aerial observation experiments are carried
out over the western Pacific area.

